-
Eva Legovic
- May 12, 2025
- 10:46 am
- Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
-
Eva Legovic
- May 12, 2025
- 10:46 am
- Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
If you clicked on this blog post, you probably already know that translation can be a messy business.
It’s a far cry from the old “c’mon, this’ll only take five minutes” mindset.
But what exactly makes translation so difficult?
And why do translators need to be more than just bilingual? Why do they often have to act as problem-solvers—fluent in tech, linguistics, and a specialized industry, with a healthy dose of general knowledge on top?
In this post, we’re unpacking why the language translation process is more complex than it looks—and what makes professional translation worth the investment.
1. Languages don’t play by the same rules
Why word-for-word translation almost always fails
One of the biggest challenges in the language translation process? Every language has its own playbook—and they don’t always translate.
Take sentence structure. English loves its Subject-Verb-Object setup (“She eats pizza”). But flip to Farsi, and suddenly it’s Subject-Object-Verb. In Arabic, the subject might even hide inside the verb. If you follow the source language too closely, you end up with weird, clunky sentences that sound like… well, Google Translate.
Then there’s grammar itself. Some languages have gendered nouns, some don’t. Some use verb aspects or articles completely differently. And that’s where translation problems begin—because grammar isn’t just structure, it’s meaning. Change it, and you risk changing what you’re trying to say.
It gets even trickier with polysemy—words that mean more than one thing. Like “date” (fruit, calendar day, romantic dinner), “light” (not heavy, illumination, or even cheerful), or “scale” (fishy or musical?). Translators have to rely on context to figure out which version makes sense. And when that context is missing? Good luck.
Oh, and don’t forget lexical gaps—those moments when a word just… doesn’t exist in the other language. English doesn’t have a direct match for “saudade” (a deep nostalgic longing) or “Schadenfreude” (pleasure at someone else’s misfortune). Translators have to get creative to fill in the blanks.
Bottom line? Literal translation often fails because language isn’t math—it’s full of nuance and shaped by culture. And that’s exactly what makes the language translation process so challenging—and so valuable when done right.
2. Culture changes everything
Because language and culture are inseparable
Here’s something that trips up even the best translation tools: language isn’t just words—it’s worldview.
What makes the language translation process truly complex isn’t just grammar or vocabulary. It’s how culture shapes meaning. A joke that lands in London might fall flat in Tokyo. A color that signals celebration in one country could signal mourning in another. Even a friendly thumbs-up can mean “up yours” in parts of the Middle East.
This is why language translation problems often stem from cultural differences—not just linguistic ones.
Let’s say your marketing copy references Thanksgiving or the Super Bowl. Or you’ve got product descriptions with idioms like “home run” or “kill two birds with one stone.” In some markets, that’ll confuse people. In others, it could offend them. That’s where localization (adapting content for local norms) and transcreation (reimagining it for emotional impact) come in.
Tone also matters. What sounds confident in one culture might feel arrogant in another. Translators have to read the room—culturally speaking—and adjust accordingly.
This is why translating isn’t just about knowing two languages. It’s about being bicultural. Without that cultural awareness, you’re not translating—you’re just swapping words and hoping for the best.
3. Idioms are chaos with a punchline
And machine translation hates them
Idioms are the ultimate curveball in the translation game. Why? Because they rarely mean what they say.
If you translate “kick the bucket” word for word, you’re not warning someone about death—you’re just describing some oddly violent bucket abuse. Same goes for “spill the beans,” “break a leg,” or “it’s a piece of cake.” Without cultural context, they make zero sense.
These language translation problems pop up in every language. In Arabic, “Ala Rasi” (literally “on my head”) means “anything for you.” In Chinese, “add feet to a snake” means you’ve ruined something by overdoing it. These aren’t phrases you can just plug into a dictionary.
So what do translators do? A few options:
- Find an equivalent idiom in the target language (best case)
- Paraphrase the meaning in plain language
- Omit it if it doesn’t add value
- Explain it, usually with a footnote (great for literature, less so for landing pages)
The trick is knowing when to translate an idiom, how to do it, and when to let it go. And that only works if you truly understand both cultures. AI? Not so much.
If you’re wondering what makes translation difficult, idioms are Exhibit A. They demand both linguistic precision and cultural intuition—something no algorithm can fake (yet).
Handling idioms well is a sign of real mastery in the language translation process.
4. Specialized content needs specialists
Because Google Translate doesn’t have a law degree
Translating everyday text is one thing. But when you’re dealing with legal contracts, medical reports, or software documentation? You need more than just language skills—you need subject matter expertise.
This is one of the biggest blind spots in the language translation process. A translator might speak fluent French and English, but when highly technical material is involved, general fluency won’t help much if they don’t understand clinical trial terminology or the finer points of GDPR compliance.
Get it wrong, and the consequences can be serious—misdiagnoses, legal disputes, broken products. That’s why translation problems often come down to one thing: the translator didn’t fully understand what they were translating.
Consistency also matters. If you call it a “user interface” in one section and “control panel” in another, your documentation gets confusing fast. That’s where glossaries and terminology databases come in. They help maintain clarity—and make you look like you’ve got your act together.
Bottom line? For high-stakes or technical content, generic translation isn’t enough. You need someone who speaks both the language and the industry.
5. Consistency is a full-time job
Especially when you’re translating at scale
If you’ve ever read a manual where the same button is called three different things… you already know why consistency matters.
In translation, inconsistency isn’t just annoying—it can confuse users, damage trust, and dilute your brand voice. And it’s one of the sneakiest challenges in the language translation process.
Here’s where things get tricky:
- Multiple translators = multiple styles
- Long-term projects = evolving terminology
- Different departments = conflicting preferences
Keeping it all aligned takes serious coordination.
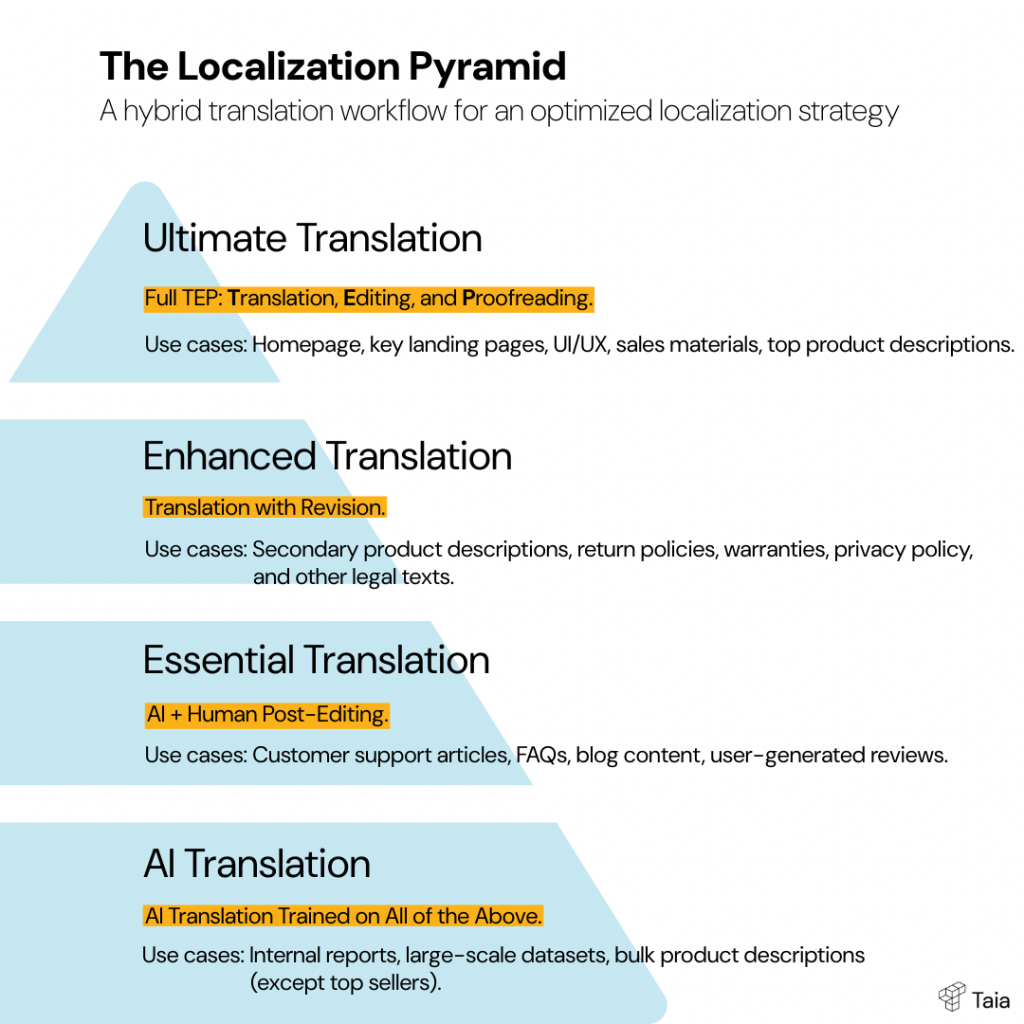
That’s why pro translators (and LSPs like us at Taia 👋) use tools like:
- Translation memories (TM) – for reusing approved segments across projects
- Glossaries – to lock in approved terms for products, features, or legal language
- Style guides – to define tone, formality, formatting, and more
But even the best tools need upkeep. A bloated TM full of outdated phrases? That’s how old mistakes come back to haunt you. So maintaining consistency isn’t just about tech—it’s about process.
Whether you’re updating FAQs, scaling content across 10 markets, or just trying to sound like one brand in every language, consistency isn’t optional. It’s essential.
Want consistency at scale? The language translation process gets a lot easier with the right tools and workflows.
6. AI translation: powerful, but not perfect
Why automation still needs a human touch
Translation tools have come a long way. AI is getting smarter. Machine translation (MT) is faster than ever. And translation memory systems can save you serious time and money on repetitive content.
In short: AI and TM tools are changing how the language translation process works.
But here’s the catch: tech can’t do it all.
Machine translation is great for speed—especially with structured, technical content. But hand it a joke, an idiom, or a bit of brand voice? You’ll get something that sounds… off. Sometimes hilariously so. Sometimes offensively so.
Translation memory helps with consistency, especially for things like legal disclaimers or product specs. But it doesn’t understand context. A reused sentence might look right—but feel totally wrong in a new paragraph.
The real trick? Knowing when to let machines handle the heavy lifting—and when a human needs to step in.
That’s why smart teams use hybrid workflows: AI for the bulk work, humans for review, creativity, and quality control. It’s faster, more cost-effective, and way more accurate than either side working alone.
In other words: technology is a tool. Not a replacement. And using it wisely is what separates good translation from a garbled mess.
7. Deadlines, budgets, and the translation pressure cooker
Welcome to the “we need it yesterday” era
If you’ve worked in content or localization, you’ve probably heard this classic line:
“Can you translate 20 pages by tomorrow? Oh, and we don’t really have a budget.”
Sound familiar?
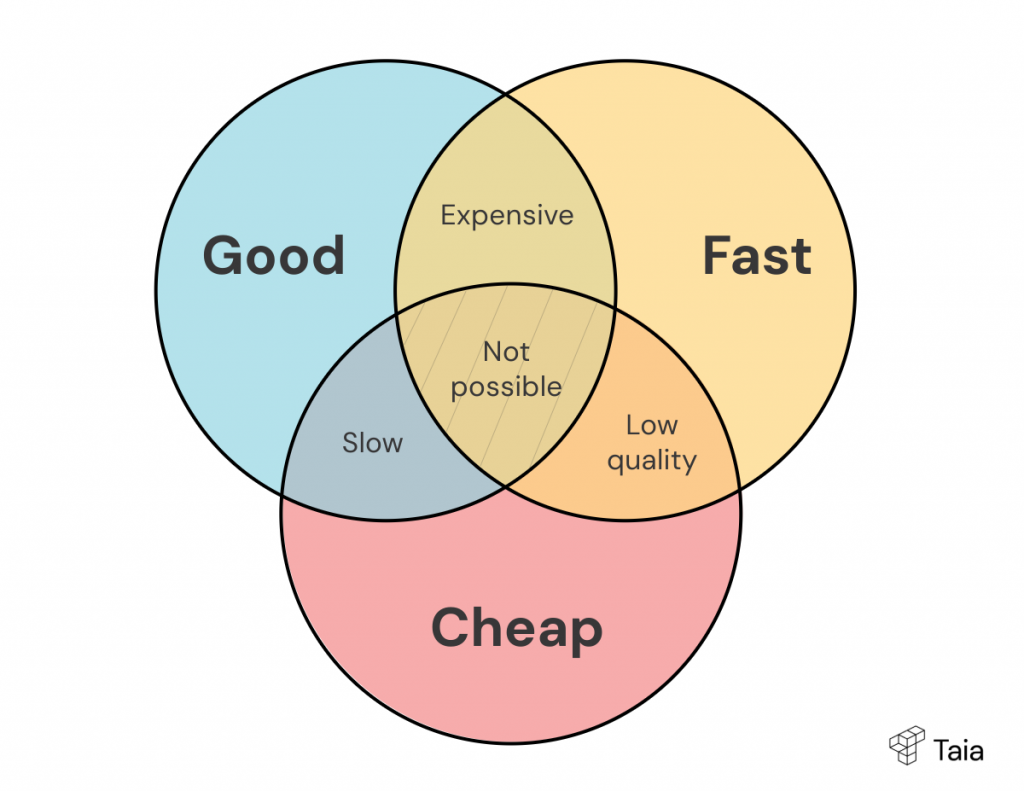
Time and money are two of the biggest constraints in the language translation process. And when both are tight (which they usually are), quality is the first thing on the chopping block.
Fast turnarounds mean less time for research, editing, or QA. Budget cuts often mean lower-cost vendors—or over-relying on machine translation without proper review. Neither ends well.
It’s the classic Iron Triangle: you can’t maximize all three at once. Push too hard on one, and the others will give.
That’s why managing translation projects isn’t just about linguistics—it’s about setting realistic expectations. The best results come when clients understand that good translation takes time, thought, and expertise. And when translators have enough breathing room to actually do their job well.
Need fast? That’s doable—with the right process and tech. Need cheap? Fine, but know where to compromise. Need flawless quality? Give it the time and budget it deserves.
8. You can’t translate what you don’t understand
Because context isn’t optional—it’s everything
Ever try translating a sentence like “bat”? Without context, is it a flying mammal, a baseball stick, or someone acting erratically?
One of the biggest pitfalls in the language translation process is working without enough background. When translators only get isolated chunks of text—with no info on who it’s for, where it’s going, or how it’s used—things get messy, fast.
Here’s what we need but don’t always get:
- A clear, well-written source text (you’d be surprised how often this is missing)
- Context about tone, audience, purpose
- Reference materials, visuals, or previous versions
Without this, translators are left guessing—and that’s where language translation problems start to snowball.
Quality also depends on robust QA. That means editing, proofreading, and validating translations before they go live. But when time or budget runs short? QA often gets skipped… and the mistakes go live instead.
💡 Pro tip: Good translation starts with good input. The clearer the source, the better the result.
9. Working with clients isn’t always smooth sailing
Because feedback isn’t always helpful (or correct)
Translation isn’t just between languages—it’s between people. And sometimes, the toughest part of the job isn’t the grammar… it’s the client.
Don’t get us wrong. Collaboration is key. But it can get complicated fast:
- Internal reviewers change mid-project and bring new preference
- Different departments argue over terminology
- Clients without language expertise suggest edits that break the translation
One of the trickiest parts of the language translation process is managing expectations. Many clients still think translation is just typing words into a tool and pressing “Go.” So when you mention tone, cultural nuance, or subject matter expertise, eyes glaze over.
That’s why education matters. The best results come from clients who:
- Provide clear, well-written source content
- Share reference materials and context
- Understand that quality takes time (and isn’t free)
Translation works best when it’s a partnership—not a handoff. The more aligned everyone is, the smoother the process, the fewer revisions, and the better the end result.
The takeaway? Translation is more than just words
It’s a process—and a surprisingly complex one.
In 2025, the language translation process is being shaped by major trends in AI, the economy, and evolving business needs.
To do it right, you need more than a bilingual brain. You need:
- Cultural fluency
- Subject matter knowledge
- The right tools (used wisely)
- Clear communication
- And yes, time and budget that match the scope
When those challenges are handled well, you get translations that build trust, drive action, and scale across markets.
And that’s where we come in.
At Taia, we blend AI speed with human precision—so you get the best of both worlds.
Our platform supports 189 languages, over 65 file types, and lets you choose the quality level that fits your content (and your budget). Whether you’re translating 10 words or 10,000, we’ll help you do it better, faster, and smarter.
👉 Try our AI document translator with a human upgrade option — it’s free to get started, no credit card required.
Frequently asked questions
Why is the language translation process so difficult?
Because translation is more than swapping words—it’s about transferring meaning across cultures, contexts, and tones. Grammar, idioms, sentence structure, and cultural expectations all vary from language to language, which makes the language translation process surprisingly complex.
What are some common pitfalls when translating from one language to another?
Common issues include mistranslating idioms, ignoring tone or context, inconsistent terminology, and overly literal translations. These are all classic language translation problems that happen when content isn’t localized or reviewed by skilled professionals.
Are there any specific phrases or terms that are tricky to translate?
Yes—idioms, culture-bound expressions, slang, and words with no direct equivalents (like “saudade” or “Schadenfreude”) are especially hard. These often require creative adaptation during the language translation process.
What makes translation difficult beyond just language?
Culture, intent, and tone play a huge role. What’s polite in one culture may be offensive in another. Translators have to bridge these gaps to make sure the message lands the right way, not just the literal way.
How do professional translators ensure consistency in large projects?
They use translation memory systems (TM), client-approved glossaries, and detailed style guides to maintain consistency in tone, terminology, and formatting—especially important in high-volume language translation processes.
Can AI solve translation problems?
AI is great for speed and repetitive content, but it still struggles with nuance, context, and brand voice. That’s why the smartest approach is a hybrid translation process—AI for efficiency, humans for accuracy.
Why do some words have no direct translation?
Because they reflect ideas that are unique to a culture. These “lexical gaps” often require explanation or localization to make sense in another language, which adds complexity to the language translation process.
What’s the difference between translation and localization?
Translation changes the language. Localization adapts the content—tone, visuals, examples, even colors—for the local culture. If translation is accuracy, localization is impact.
What are real examples of language translation problems?
Think of a website where a CTA sounds rude, or a product label that’s mistranslated and confusing. These errors often come from ignoring tone, cultural nuance, or the intent behind the words.
How can I make sure my content is translated properly?
Work with professionals who understand your industry, provide clear source material and context, and choose a translation quality tier that fits the content’s importance. Tools help, but people make it work.